RAPID & DURABLE
DISEASE CONTROL IN nr-axSpA1-3
Not an actual AS or nr-axSpA patient
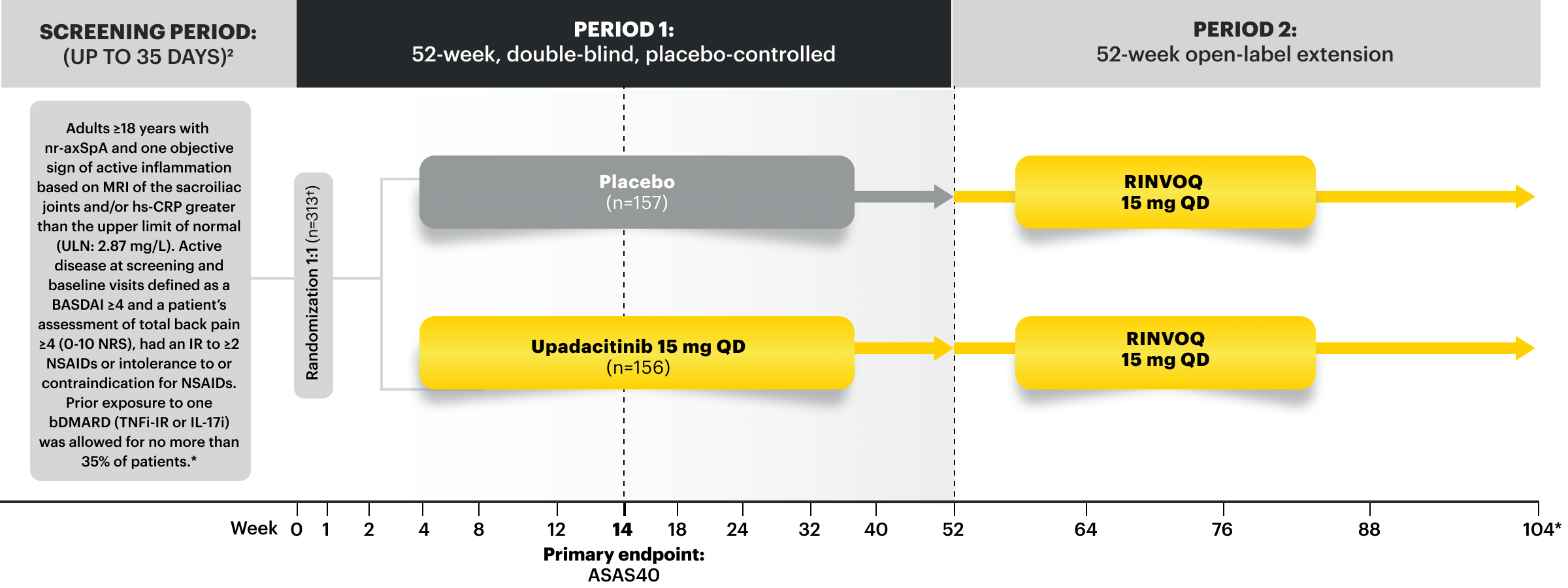
RINVOQ achieved its primary endpoint of ASAS40 at Week 14 vs placebo,
and responses observed at Week 2, up to 2 years1-3
INDICATION
RINVOQ is indicated for the treatment of adults with active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) with objective signs of inflammation who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker therapy.
Limitations of Use: RINVOQ is not recommended for use in combination with other Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine.
SELECT-AXIS 2 Study 2: nr‑axSpA (mixed* biologic)1,2,4
RINVOQ 15 mg (n=156), Placebo (n=157)
ASAS40 at Week 14 (NRI-MI)
44.9%† RINVOQ vs 22.3% Placebo at Week 14
PRIMARY ENDPOINT
*Mixed=67% bDMARD-naïve & 33% bDMARD-IR.
†P<0.0001.5
RINVOQ is indicated for TNFi-IR patients.
SELECT-AXIS 2 Study 2: nr-axSpA Design Intro:
52-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 3 study of 313 patients with nr-axSpA and one objective sign of active inflammation based on MRI of the sacroiliac joints and/or hs-CRP greater than the upper limit of normal (ULN; 2.87 mg/L). Patients had an intolerance or inadequate response to at least 2 NSAIDs and, in 33%, to 1 bDMARD. Patients were randomized to receive RINVOQ 15 mg once daily or placebo. Patients could continue background NSAIDs.1,2
Please see Important Safety Information, including BOXED WARNING on Serious Infections, Mortality, Malignancies, Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events, and Thrombosis, below.
NRI-MI Data From SELECT-AXIS 2 Study 2: nr-axSpA (mixed*)2,3
RINVOQ 15 mg (n=156), Placebo (n=157)
ASDAS-CRP at Week 14
42 %† RINVOQ vs 18% Placebo
RANKED SECONDARY ENDPOINT
ASDAS-CRP Inactive Disease at Week 14
14%† RINVOQ vs 5% Placebo
RANKED SECONDARY ENDPOINT
*Mixed=67% bDMARD-naïve and 33% DMARD-IR.
†P<0.0001.
SELECT-AXIS 2 Study 2: nr-axSpA ASDAS-CRP LDA and rates up to 2 years3
ALL DATA AS OBSERVED (AO)
A study in mixed* biologic patients.
75% of RINVOQ nr-axSpA Patients Achieved LDA at 2 Years3
RINVOQ is indicated for TNFi-IR patients.
All data are as observed cases.
*Mixed=67% bDMARD-naïve and 33% bDMARD-IR.2
All data are as observed cases.
In an As Observed (AO) analysis, patients with missing data at a specific time are not included, which may enrich the population and increase the response rates.
OLE LIMITATIONS: There is potential for enrichment of OLE data; unblinding patients may cause bias related to overall treatment effect.
Get a summary of the Low Disease Activity Data
Achieving ASDAS-Low Disease Activity May Indicate Disease Control—Making It a Measure to Strive for in Patients With AS or nr-axSpA2,3,6,7
ASDAS-CRP Disease Activity State Components
The ASDAS-CRP score is a composite measure that assesses common patient symptoms and an objective sign of inflammation. The score is calculated by assessing the following components6:
Back Pain
Duration of Morning Stiffness
Patient Global Assessment
Peripheral Joint Pain/Swelling
Inflammation (CRP)
SELECT-AXIS 2 Study 2: nr-axSpA (mixed*)
Distribution of RINVOQ Patients by ASDAS-CRP State
ALL DATA AS OBSERVED (AO)
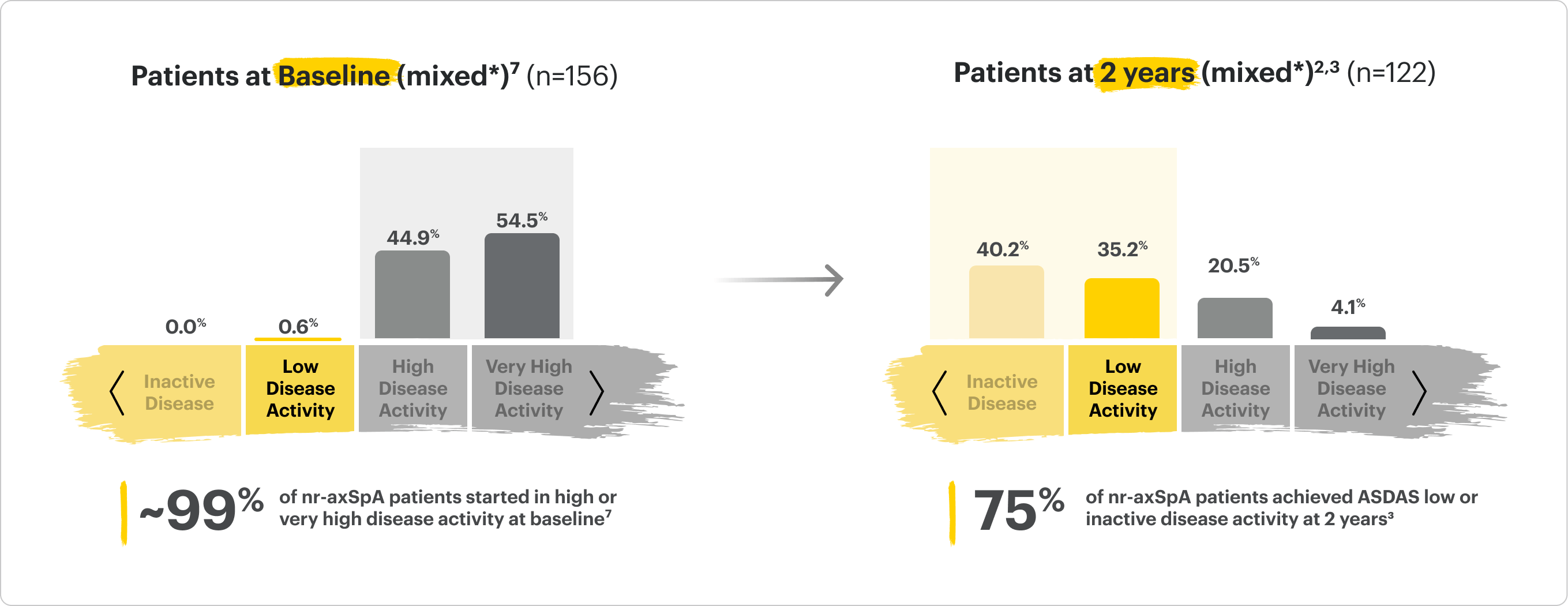
*Mixed=67% bDMARD-naïve & 33% bDMARD-IR2
Safety Considerations
Serious Infections: RINVOQ-treated patients are at increased risk of serious bacterial (including tuberculosis [TB]), fungal, viral, and opportunistic infections leading to hospitalization or death. Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants, such as methotrexate or corticosteroids.
Mortality: A higher rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular (CV) death, was observed with a Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) in a study comparing another JAKi with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients ≥50 years with ≥1 CV risk factor.
Malignancies: Malignancies have occurred in RINVOQ-treated patients. A higher rate of lymphomas and lung cancer (in current or past smokers) was observed with another JAKi when compared with TNF blockers in RA patients.
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events: A higher rate of CV death, myocardial infarction, and stroke was observed with a JAKi in a study comparing another JAKi with TNF blockers in RA patients ≥50 years with ≥1 CV risk factor. History of smoking increases risk.
Thrombosis: Deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and arterial thrombosis have occurred in patients treated with JAK inhibitors used to treat inflammatory conditions. A higher rate of thrombosis was observed with another JAKi when compared with TNF blockers in RA patients.
Hypersensitivity: RINVOQ is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to RINVOQ or its excipients.
Other Serious Adverse Reactions: Hypersensitivity Reactions, Gastrointestinal Perforations, Laboratory Abnormalities, and Embryo-Fetal Toxicity.
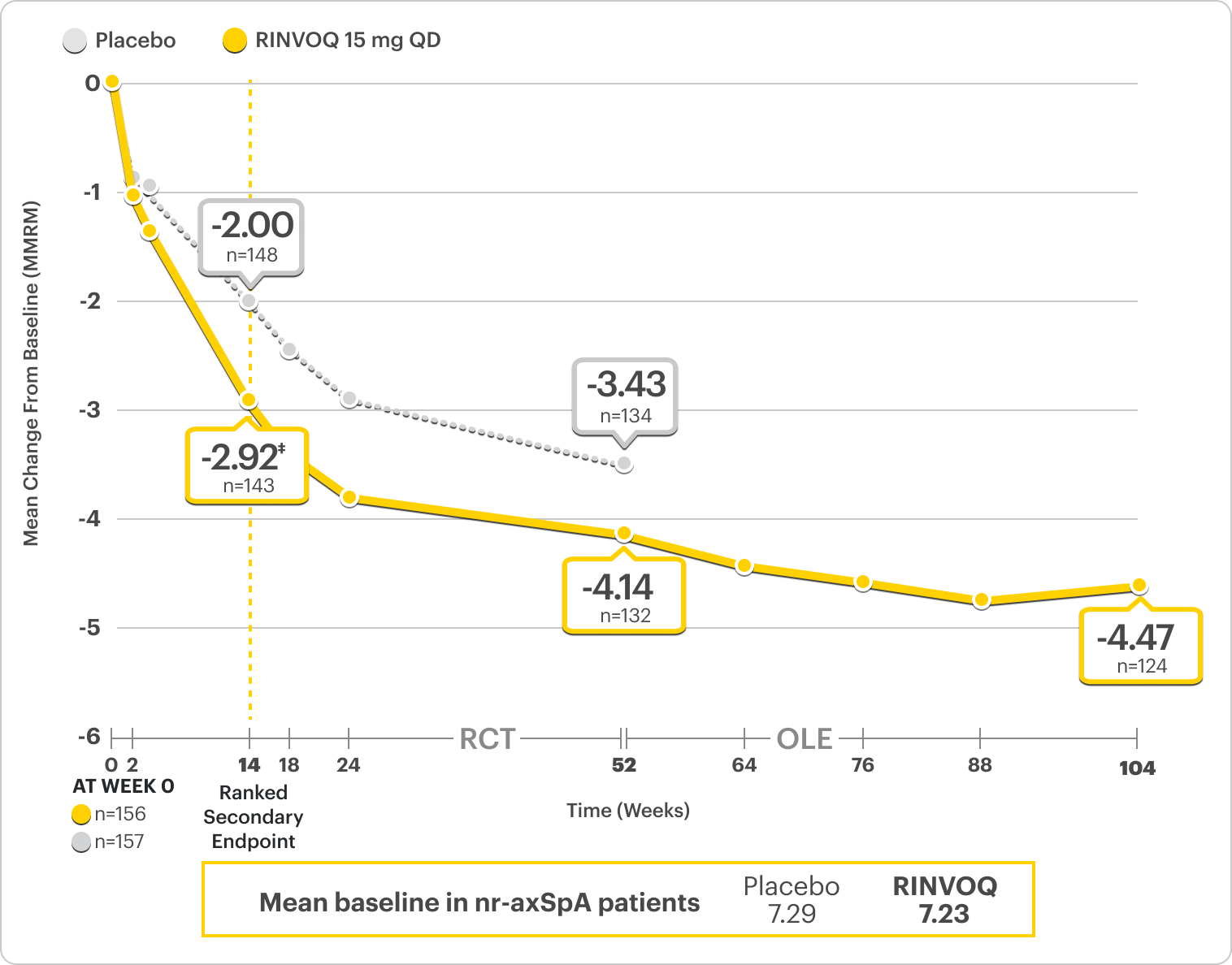
Improvement in Total Back Pain and Nocturnal Back Pain
ΔTotal Back Pain ranked secondary endpoint at Week 14 with response rates up to 2 years2,3
SELECT-AXIS 2 Study 2: nr-axSpA ΔTotal Back Pain From Baseline Up to 2 Years (MMRM)2,3,*
A study in mixed† biologic patients
RINVOQ is indicated for TNFi-IR patients.
*Mixed=67% bDMARD-naïve & 33% bDMARD-IR.2
†Total back pain defined on a numeric rating scale (0–10) based on the following question: “What is the amount of back pain that you experienced at any time during the last week?”2
‡P=0.0004.2
41% improvement (n=143) vs 28% (n=148) with placebo at Week 14 as observed and 64% improvement (n=124) at 2 years as observed3,8
DATA LIMITATIONS: Data labeled as ranked secondary endpoints at Week 14 were multiplicity-controlled for comparisons. All other comparisons were not adjusted for multiplicity; therefore, statistical significance has not been established.3
OLE LIMITATIONS: There is potential for enrichment of OLE data; unblinding patients may cause bias related to overall treatment effect.
ΔNocturnal Back Pain ranked secondary endpoint at Week 14 with response rates up to 2 years2,3
SELECT-AXIS 2 Study 2: nr-axSpA ΔNocturnal Back Pain From Baseline Up to 2 Years (MMRM)2,3,*
A study in mixed† biologic patients
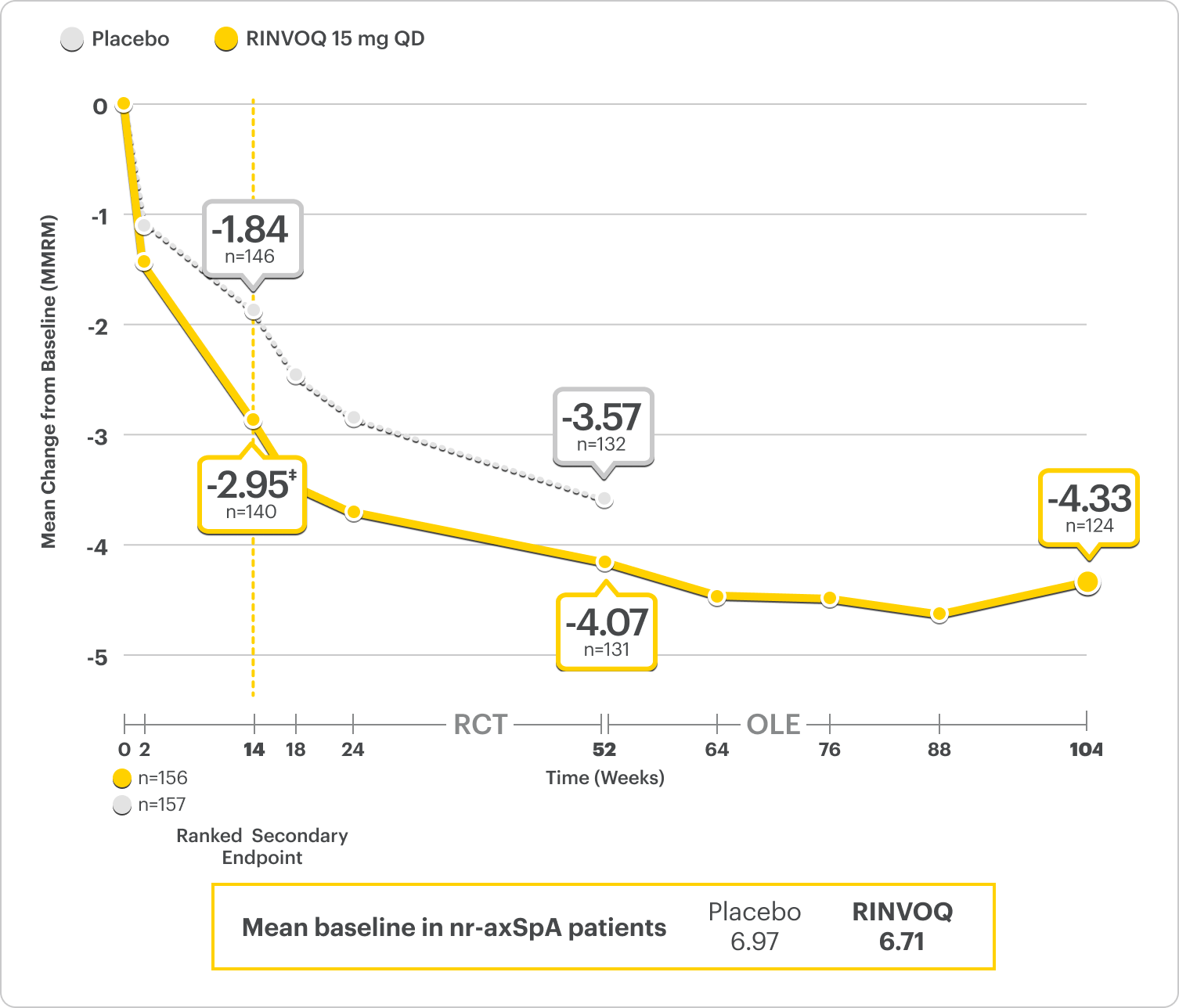
RINVOQ is indicated for TNFi-IR patients.
*Nocturnal back pain defined on a numeric rating scale (0–10) based on the following question: “What is the amount of back pain at night that you experienced during the last week?”6
†Mixed=67% bDMARD-naïve & 33% bDMARD-IR.2
‡P<0.001.2
44% improvement (n=138) vs 26% (n=146) with placebo at Week 14 as observed and 62% improvement (n=130) at 1 year as observed8
DATA LIMITATIONS: Data labeled as ranked secondary endpoint at Week 14 were multiplicity-controlled for comparisons. All other comparisons were not adjusted for multiplicity; therefore, statistical significance has not been established.2
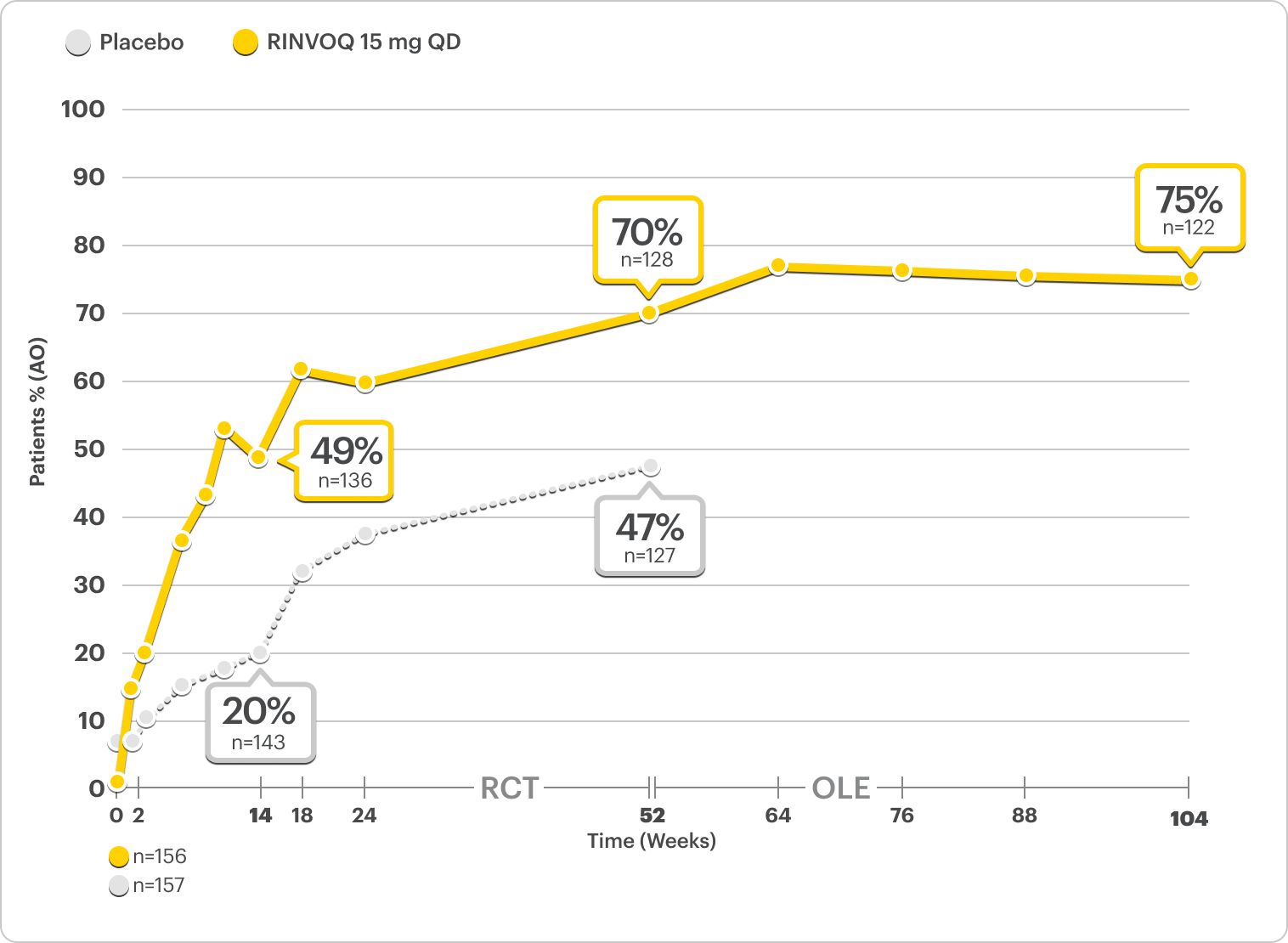
Durable Rates of ASAS40 Response Up to 2 Years
SELECT-AXIS 2 Study 2: nr-axSpA ASAS40 Response Up to 2 Years1-3
ALL DATA AS OBSERVED (AO)
A study in mixed* biologic patients.
72% of RINVOQ nr-axSpA Patients Achieved ASAS40 at 2 Years3
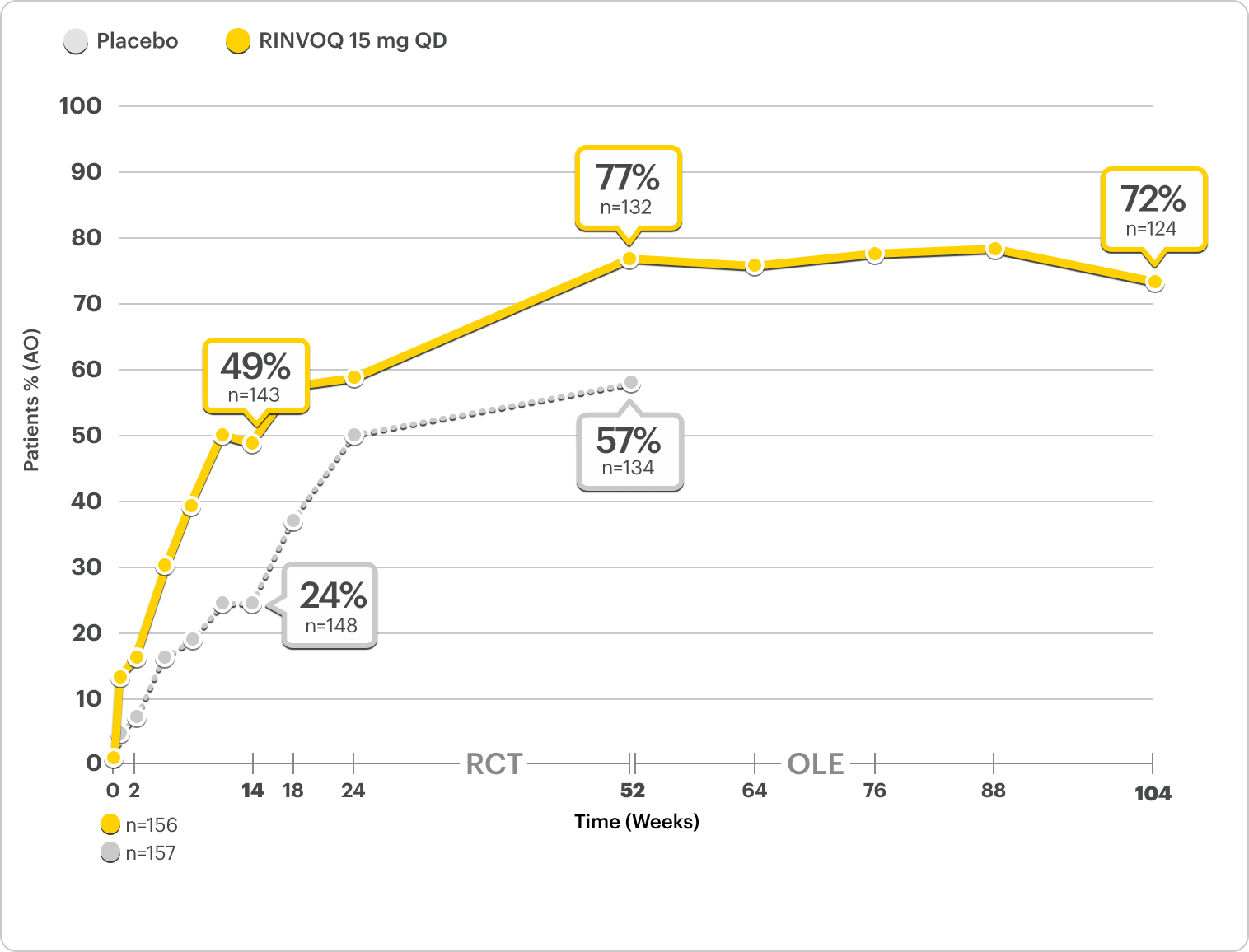
RINVOQ is indicated for TNFi-IR patients.
All data are as observed cases.
*Mixed=67% bDMARD-naïve and 33% bDMARD-IR.2
†Total back pain defined on an NRS (0-10) based on the following question: "What is the amount of back pain that you experienced at any time during the last week?"2
‡Mean score of BASDAI questions 5 and 6 on severity and duration of morning stiffness.2
In an As Observed (AO) analysis, patients with missing data at a specific time are not included, which may enrich the population and increase the response rates.
OLE LIMITATIONS: There is potential for enrichment of OLE data; unblinding patients may cause bias related to overall treatment effect.
ASAS40 reflects a ≥40% improvement in 3 of the 4 following domains with no worsening in the fourth domain2:
ASAS Domains
- Total back pain†
- Inflammation (Morning Stiffness)‡
- Physical function (BASFI)
- Patient Global Assessment of disease activity

Interested in the safety data for RINVOQ?
See RINVOQ’s safety data across clinical trials