DISRUPT THE
SIGNAL
WITH JAK INHIBITION
For adults with giant cell arteritis (GCA) and for adult TNFi-IR patients with: moderate to severe ulcerative colitis (UC); moderate to severe Crohn's disease (CD); moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA); active psoriatic arthritis (PsA); active ankylosing spondylitis (AS); or active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) with objective signs of inflammation.
For the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with refractory, moderate to severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with other systemic drug products, including biologics, or when use of those therapies are inadvisable.1
For the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with active psoriatic arthritis and active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.1
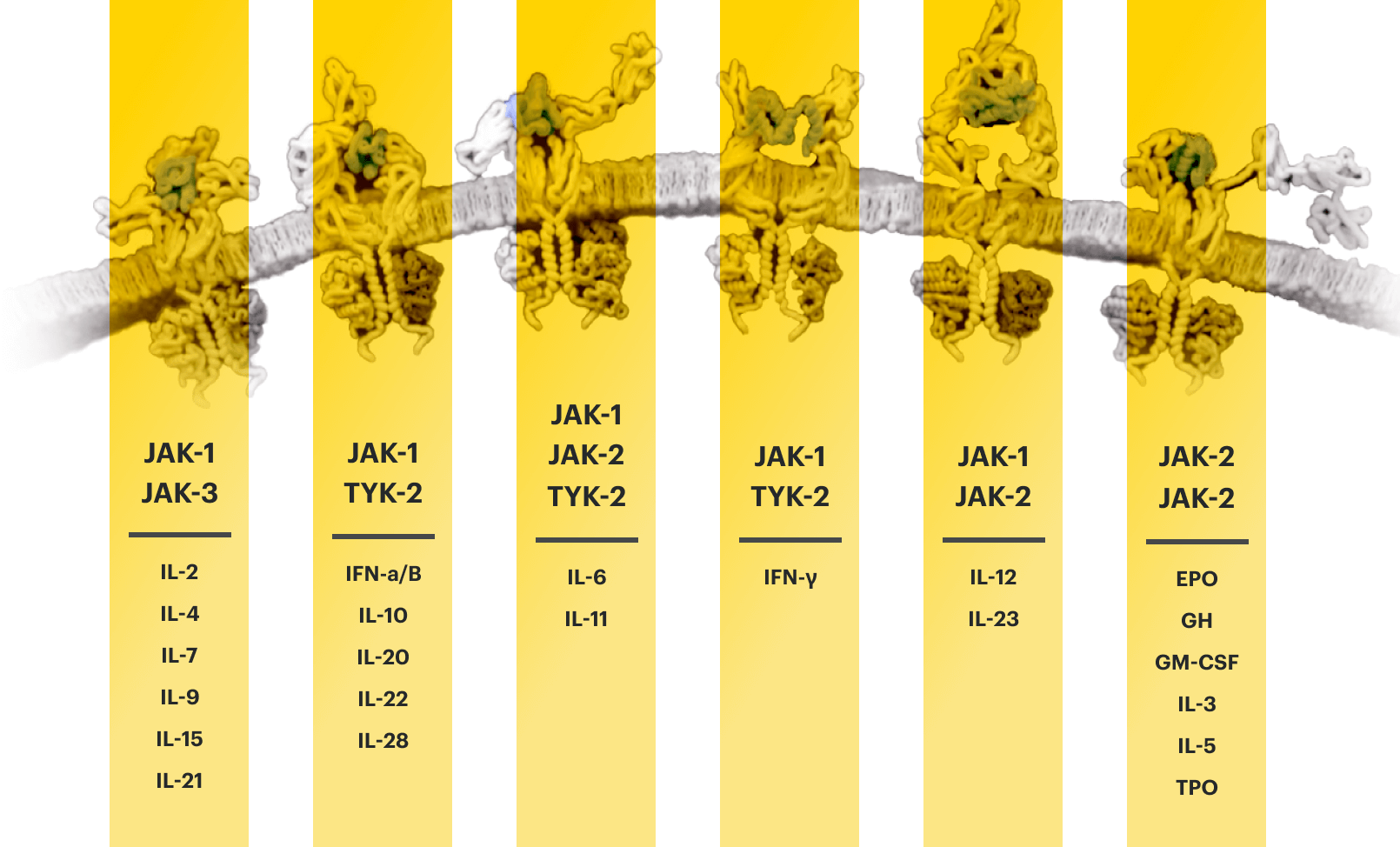
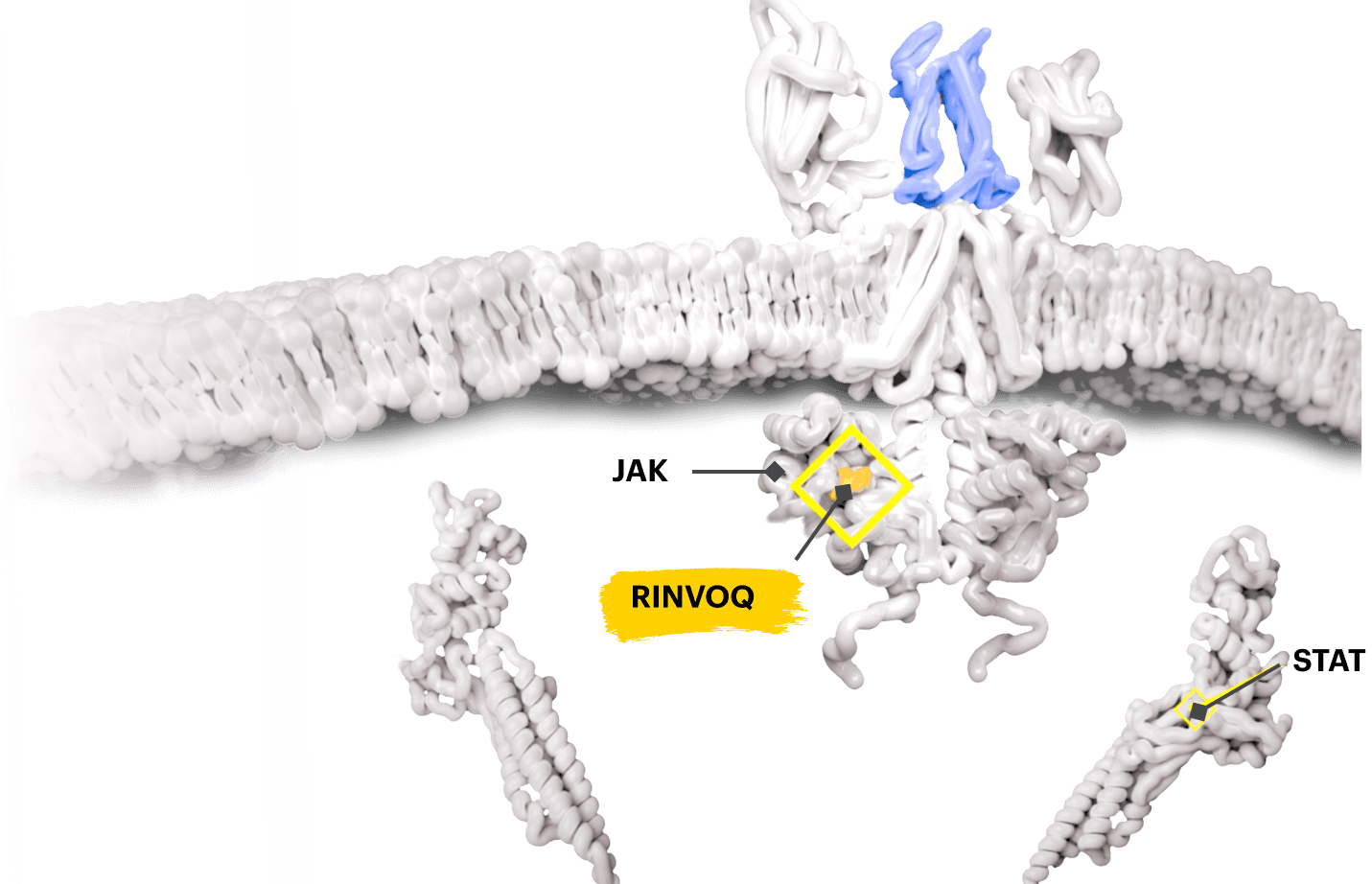
Overview of the JAK-STAT pathway
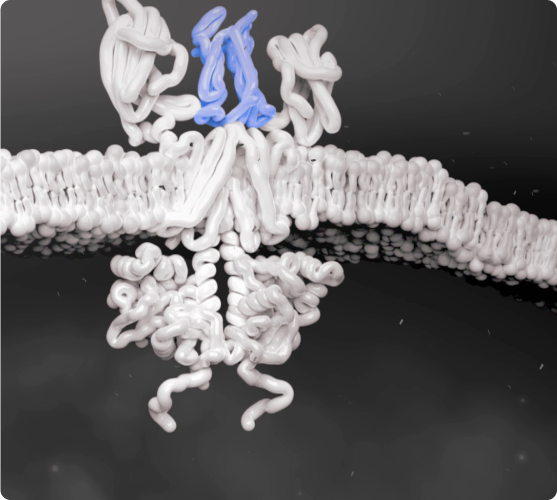
Cytokines Bind to Cells
Several key cytokines are thought to use signaling networks such as the JAK-STAT pathway. Overexpression of these key cytokines can lead to excess inflammation.1-4
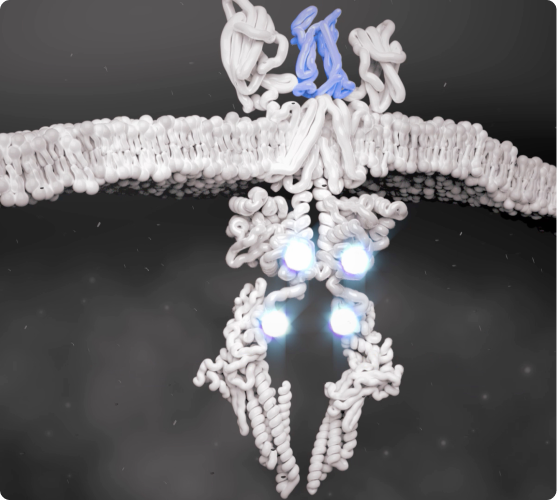
JAK-STAT Pathway Is Activated
Cytokines that bind to the cell receptors trigger JAK recruitment, which then activates STAT—a process that signals the cell nucleus to initiate the inflammatory response.2,5,6
Inflammatory Response Is Triggered
Once the JAK-STAT pathway has been activated by certain cytokines, the inflammatory response is initiated and continues a cycle of pathologic inflammation.7,8
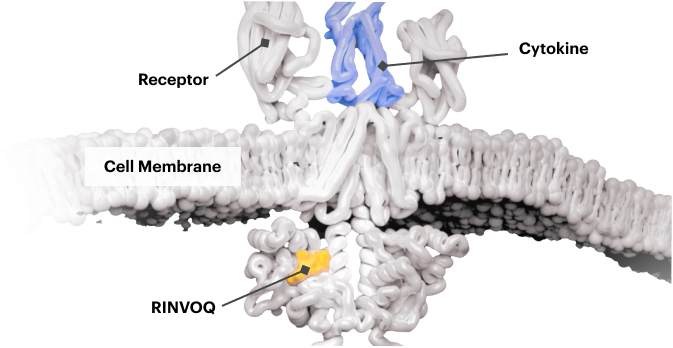
Block the JAK-STAT Pathway With RINVOQ—a JAK Inhibitor
By inactivating JAK, RINVOQ is thought to block the recruitment, phosphorylation, and activation of STATs, preventing the pro‑inflammatory cytokine signal from reaching the nucleus and inhibiting pro‑inflammatory processes associated with the JAK‑STAT pathway.1,8,9
Based on enzymatic and cellular assays, RINVOQ demonstrated greater inhibitory potency at JAK1 and JAK2 vs JAK3 and TYK2.1
The relevance of inhibition of specific JAK enzymes to therapeutic effectiveness is not currently known.1
EPO=erythropoietin; GH=growth hormone; GM‑CSF=granulocyte‑macrophage colony‑stimulating factor; IFN=interferon; IL=interleukin; IR=intolerance or inadequate response; JAK=Janus kinase; STAT=signal transducer and activator of transcription; TNFi=tumor necrosis factor inhibitor; TPO=thrombopoietin; TYK=tyrosine kinase.




